我国拟限制磷酸铁锂/磷酸锰铁锂等制备技术出口
近日,中国商务部发布“关于《中国禁止出口限制出口技术目录》(简称“目录”)调整公开征求意见的通知”。其中,拟增加对磷酸铁锂、磷酸锰铁锂及磷酸盐正极原材料的制备技术的出口限制。意见反馈截止时间为2025年2月1日。
具体来看,在限制出口部分,拟新增电池正极材料制备技术(编号:252604X),控制要点如下所示:
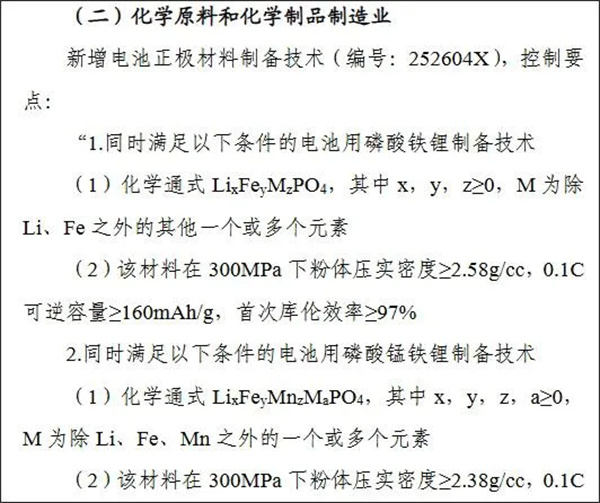
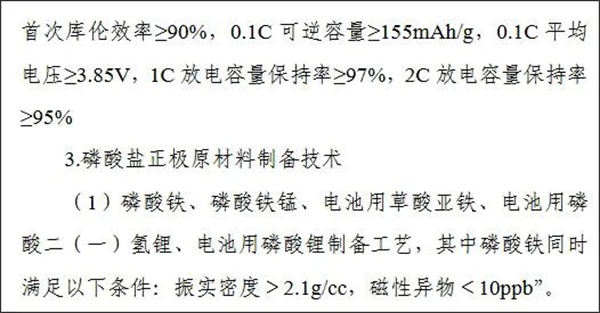
也就是说,调整后的新规,可能将上述满足一定条件的电池正极材料的制备技术,列入到“化学原料和化学制品制造业”的限制出口类目之中。同时,此次通知明确指出,相关调整的目的是“为加强国际技术交流合作创造积极条件”。
在此背景下,如果未来实施上述调整,将会对电池产业产生怎样的影响?
01
现状:磷酸铁锂电池装机热潮席卷全球,
磷酸锰铁锂电池能量密度比肩中镍三元
业界周知,锂电池正极材料是锂电池的关键材料之一,对锂电池的核心性能和制造成本等影响较大。目前,市场上形成规模化应用的锂电池正极材料包括磷酸铁锂、三元、磷酸锰铁锂等。
其中,磷酸铁锂和三元材料占据较大的市场规模,同时,磷酸锰铁锂因其优异性能和较低成本优势,正快速崛起,多家电池、材料企业已经深度布局。
动力电池应用分会数据显示,2024年1-11月,在中国市场473GWh的动力电池总装机数据中,磷酸铁锂电池装机量高达348GWh,市占率接近3/4,彰显了其主导地位。值得注意的是,同期磷酸铁锂装机量同比增长超51.5%,比三元锂电池高出37.8个百分点。
凭借高安全、长循环寿命和成本优势,磷酸铁锂电池不仅在中国新能源汽车市场成为主流,还获得海外动力、储能市场的高度关注。
海外市场方面,Stellantis、通用、现代、大众等国际车企,均已表明将在其入门级车型中导入LFP电池,雷诺更是在2024年7月下发39GWh的磷酸铁锂电池采购订单。同时,海外储能系统集成商也越来越青睐磷酸铁锂电池,以逐步取代原来由日韩电池企业主导的三元锂电池体系。
据预测,到2030年,仅欧洲动力和储能电池总需求就将达到1500GWh,其中约有一半,也即750GWh将采用磷酸铁锂电池,市场规模庞大。
同时,磷酸铁锂的“升级版”——磷酸锰铁锂,作为一种新型正极材料,其市场潜力也在快速增长。
业界人士表示,目前磷酸锰铁锂电池的能量密度,已接近中镍三元锂电池水平,但其价格有望与磷酸铁锂电池持平。
实际上,随着材料改性技术的不断进步,叠加锰基材料具有锰源丰富、成本低廉、适配高电压、倍率性能及低温性能好等特点,锰基正极材料已受到特斯拉、宁德时代、亿纬锂能、瑞浦兰钧、力神电池、孚能科技、国轩高科、欣旺达、克能新能源等新能源企业的高度关注,并已经成为很多企业电池研发和规模化应用的一个重要方向。
整体看,我国磷酸铁锂正极材料的生产在全球占据主导地位。数据显示,当前全球90%的磷酸铁锂正极材料由中国公司生产。磷酸锰铁锂虽然市场占比目前还相对较小,但作为中国优势技术,其在未来具有广阔的发展空间。因此,这两种材料,以及磷酸盐等前驱体的制备技术,受到全球新能源企业的广泛关注,也成为海外电池及正极企业布局和竞争的重点。
02
六大影响猜想
如果未来我国限制上述技术出口,或将带来以下几个方面的影响:
一是,进一步提高我国电池产品竞争力。
我国在磷酸铁锂、磷酸锰铁锂正极及磷酸盐等前驱体制备技术方面,具有较高优势,限制相关先进技术出口,可使国内材料及电池企业,在全球市场保持技术领先地位,形成技术“护城河”,降低在海外市场的竞争压力,有助于我国企业在国际市场上保持利润空间和市场份额。
二是,巩固产业主导权,提高话语权。
受益于磷酸铁锂及前驱体供应链和制备技术的优势,我国磷酸铁锂电池产能和供给领跑全球,限制相关技术出口,能够进一步巩固我国在全球新能源产业中的主导权,提升我国在国际产业链中的话语权和影响力。
三是,引导国内企业注重技术创新,提高产业附加值。
限制相关技术出口,将引导国内企业意识到核心技术的重要性和保密性。为保持全球竞争优势,国内企业有望加大对磷酸铁锂、磷酸锰铁锂技术的创新研发投入,积极探索新的生产工艺,进一步提高产品性能和质量,助力产业升级。
同时,引导企业将高附加值技术在国内转化应用,提高我国锂电产业的附加值和经济效益,促进我国新能源产业的集群化发展。
四是,从动力到储能领域,拓宽市场。
这些技术不仅是汽车用动力电池的重要技术,也是储能领域的关键技术。限制相关技术的出口,有利于我国企业拓展海外储能市场,并确保国内电池材料供应的稳定性。
五是,保持前沿技术优势。
业界人士指出,此次拟调整目录所涉及的磷酸铁锂、磷酸锰铁锂制备技术控制参数较高,属下一代技术,目前尚未大规模应用,仍处于攻关和小批量应用阶段。
限制先进技术出口,可以避免前沿技术过早地流向海外市场,以保障我国在大规模应用阶段具备核心技术储备优势,从而促进我国电池产业的健康发展。
六是,国际合作需报备,海外下游企业或寻替代方案。
目录调整拟对相关技术出口实施限制,并非禁止。业内人士表示,在经过地方商务主管部门相关许可审批后,企业或仍可以进行技术出口。
另一方面,其它国家对磷酸铁锂电池尚未实现规模化量产,相关正极材料产能也较为匮乏,部分海外下游企业或有望加大对我国磷酸铁锂电池及正极材料的采购力度,以保持其整车的市场竞争力。同时,海外企业也可能加速寻找替代方案,以减少对中国的依赖。
Recently, the Chinese Ministry of Commerce issued a notice soliciting public opinions on the adjustment of the "Catalogue of Technologies Prohibited and Restricted from Export in China" (referred to as the "Catalogue"). Among them, it is proposed to increase export restrictions on the preparation technology of lithium iron phosphate, lithium manganese iron phosphate, and phosphate cathode raw materials. The deadline for feedback is February 1, 2025.
Specifically, in the restricted export section, a new battery positive electrode material preparation technology (No. 252604X) is proposed, with the following control points:
China plans to restrict the export of preparation technologies such as lithium iron phosphate/lithium manganese iron phosphate
China plans to restrict the export of preparation technologies such as lithium iron phosphate/lithium manganese iron phosphate
That is to say, the adjusted new regulations may include the preparation technology of battery positive electrode materials that meet certain conditions in the restricted export category of "chemical raw materials and chemical products manufacturing industry". At the same time, this notice clearly states that the purpose of the relevant adjustments is to "create positive conditions for strengthening international technological exchanges and cooperation".
In this context, what impact will the above adjustments have on the battery industry in the future?
01
Current situation: The trend of installing lithium iron phosphate batteries is sweeping the world,
The energy density of lithium manganese iron phosphate batteries is comparable to that of nickel ternary batteries
As is well known in the industry, the positive electrode material of lithium batteries is one of the key materials, which has a significant impact on the core performance and manufacturing cost of lithium batteries. At present, the lithium battery cathode materials that have formed large-scale applications in the market include lithium iron phosphate, ternary, manganese iron phosphate lithium, etc.
Among them, lithium iron phosphate and ternary materials occupy a large market size. At the same time, lithium manganese iron phosphate is rapidly rising due to its excellent performance and lower cost advantages, and multiple battery and material companies have already made deep layouts.
According to data from the Power Battery Application Branch, from January to November 2024, in the total installed capacity of 473GWh of power batteries in the Chinese market, the installed capacity of lithium iron phosphate batteries reached 348GWh, with a market share of nearly 3/4, demonstrating its dominant position. It is worth noting that during the same period, the installed capacity of lithium iron phosphate increased by over 51.5% year-on-year, which is 37.8 percentage points higher than that of ternary lithium batteries.
With high safety, long cycle life, and cost advantages, lithium iron phosphate batteries have not only become mainstream in the Chinese new energy vehicle market, but also received high attention from overseas power and energy storage markets.
In terms of overseas markets, Stellantis、 International car companies such as General Motors, Hyundai, and Volkswagen have all stated their intention to introduce LFP batteries into their entry-level models, and Renault has placed a purchase order for 39GWh lithium iron phosphate batteries in July 2024. Meanwhile, overseas energy storage system integrators are increasingly favoring lithium iron phosphate batteries to gradually replace the ternary lithium battery system previously dominated by Japanese and Korean battery companies.
It is predicted that by 2030, the total demand for power and energy storage batteries in Europe alone will reach 1500 GWh, of which about half, or 750 GWh, will use lithium iron phosphate batteries, with a huge market size.
At the same time, the upgraded version of lithium iron phosphate - lithium manganese iron phosphate, as a new type of positive electrode material, has a rapidly growing market potential.
Industry insiders have stated that the energy density of manganese iron phosphate lithium batteries is currently close to the level of medium nickel ternary lithium batteries, but their price is expected to be on par with lithium iron phosphate batteries.
In fact, with the continuous advancement of material modification technology, manganese based materials have the characteristics of abundant manganese sources, low cost, adaptability to high voltage, good rate performance, and low temperature performance. Manganese based positive electrode materials have received high attention from new energy enterprises such as Tesla, CATL, EVE Energy, Ruipu Lanjun, Lishen Battery, Funeng Technology, Guoxuan High tech, Xinwangda, and Keneng New Energy, and have become an important direction for battery research and development and large-scale application in many enterprises.
Overall, the production of lithium iron phosphate cathode materials in China dominates the world. Data shows that currently 90% of lithium iron phosphate cathode materials worldwide are produced by Chinese companies. Although the market share of lithium manganese iron phosphate is relatively small at present, as a dominant technology in China, it has broad development space in the future. Therefore, these two materials, as well as the preparation technology of precursors such as phosphates, have received widespread attention from global new energy companies and have become a key focus of overseas battery and cathode companies' layout and competition.
02
Six major impact hypotheses
If China restricts the export of the above-mentioned technologies in the future, it may have the following impacts:
One is to further enhance the competitiveness of China's battery products.
China has a high advantage in the preparation technology of lithium iron phosphate, lithium manganese iron phosphate cathodes, and phosphate precursors. Restricting the export of related advanced technologies can enable domestic material and battery enterprises to maintain a leading position in the global market, form a technological "moat", reduce competition pressure in overseas markets, and help Chinese enterprises maintain profit margins and market share in the international market.
Secondly, we need to consolidate our dominant position in the industry and enhance our discourse power.
Benefiting from the advantages of the supply chain and preparation technology of lithium iron phosphate and its precursors, China leads the world in terms of production capacity and supply of lithium iron phosphate batteries. Restricting the export of related technologies can further consolidate China's leading position in the global new energy industry and enhance its discourse power and influence in the international industrial chain.
Thirdly, guide domestic enterprises to focus on technological innovation and increase industrial added value.
Restricting the export of related technologies will guide domestic enterprises to realize the importance and confidentiality of core technologies. To maintain a global competitive advantage, domestic enterprises are expected to increase their investment in innovative research and development of lithium iron phosphate and lithium manganese phosphate technologies, actively explore new production processes, further improve product performance and quality, and assist in industrial upgrading.
At the same time, guide enterprises to transform and apply high value-added technologies domestically, improve the added value and economic benefits of China's lithium battery industry, and promote the cluster development of China's new energy industry.
Fourthly, expanding the market from power to energy storage.
These technologies are not only important technologies for automotive power batteries, but also key technologies in the field of energy storage. Restricting the export of related technologies is beneficial for Chinese enterprises to expand their overseas energy storage markets and ensure the stability of domestic battery material supply.
Fifth, maintain the advantage of cutting-edge technology.
Industry insiders pointed out that the preparation technology control parameters of lithium iron phosphate and lithium manganese iron phosphate involved in the proposed adjustment of the catalog are relatively high, and their next-generation technologies have not yet been widely applied and are still in the stage of research and small-scale application.
Restricting the export of advanced technologies can prevent the premature flow of cutting-edge technologies to overseas markets, ensuring that China has a core technological reserve advantage in the large-scale application stage and promoting the healthy development of China's battery industry.
Sixth, international cooperation needs to be reported, and overseas downstream enterprises may seek alternative solutions.
The directory adjustment intends to impose restrictions on the export of related technologies, not prohibitions. Industry insiders indicate that companies may still be able to export technology after obtaining relevant permits and approvals from local commerce authorities.
On the other hand, other countries have not yet achieved large-scale production of lithium iron phosphate batteries, and the production capacity of related positive electrode materials is also relatively scarce. Some overseas downstream enterprises may increase their procurement efforts for China's lithium iron phosphate batteries and positive electrode materials to maintain their overall market competitiveness. Meanwhile, overseas companies may also accelerate their search for alternative solutions to reduce their dependence on China.
It can be seen that through this adjustment of the directory, it will be beneficial to maintain the advantages of China's new energy industry and guide domestic battery industry chain enterprises to go global in an orderly manner.

